[Disclosure: Please assume all outbound links may in some cases provide site-sustaining revenue from ads or referrals (with never any extra costs to you). See footer for more details. Thank you]
How to Test for Radon Gas
The Best Radon Testing Kit and Digital Detector for Your Home
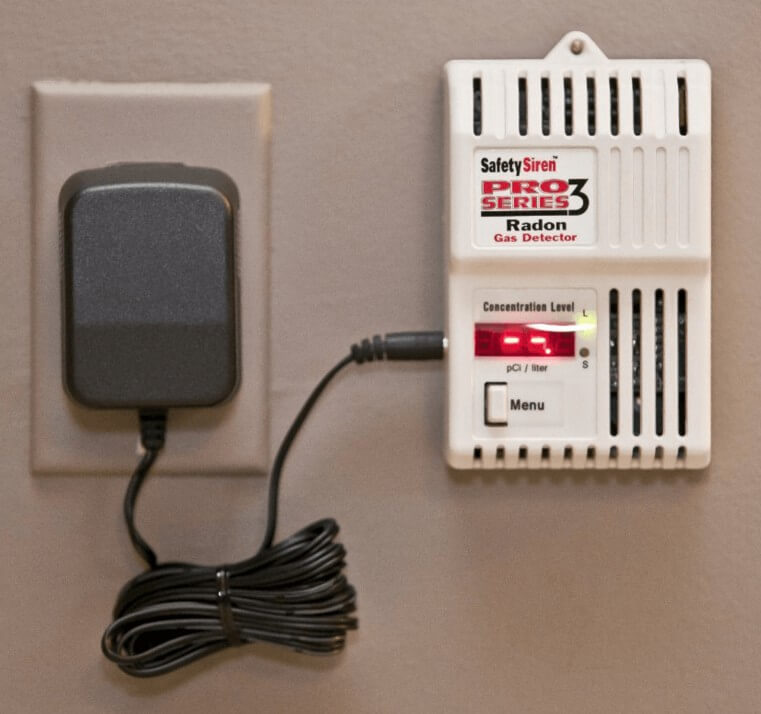

If you are wondering how to test for Radon Gas in your home, keep in mind there are two main types of Radon gas detectors - passive devices and active devices.
Passive Radon test kits are usually cheaper canisters which contain Radon gas detection material. You place the kit in your home for a time, then send it back to a lab which will provide a Radon result to you.
Actives on the other hand, are more sophisticated electronic Radon detectors, either plug-in or battery operated. They actively monitor Radon levels real-time. And active monitors can provide short and long-term average readings, plus sound an alarm to signal when Radon level exceeds a preset limit, such as the national action level of 4 pCi/L (more about Radon concentrations below).
Passive devices require no electricity to run the test and tend to be cheaper. But they are often charcoal based, which can be less accurate in high humidity situations. And unlike an active electronic Radon tester, passive test kits provide more of an average "snapshot", rather a real-time or on-going readout of what your in-home radon levels may be.
BUT because you ship the passive-type canisters back to an accredited Radon testing lab and receive back a formal test result in black and white, you have the benefit of documentation. A documented accredited Radon test result is increasingly necessary in circumstances such as appeasing buyers looking to purchase your home, especially in high risk Radon areas where Radon inspection and disclosure has become common.
There are several different classes of passive devices:
- Electret ion chamber detectors (short-term testing device available only through laboratories)
- Charcoal liquid scintillation detectors (LS Vials are usually for short term 2 to 4 day testing)
- Charcoal canisters (usually for shorter term testing)
- Alpha track detectors (Usually for longer term testing) <= I used the top-rated kit of this type to get a long-term 195 day test result for my house, see my results below
The cheaper passive Radon test kits usually include the return shipping package so you can send the canisters back to a certified radon testing lab which will perform the analysis and then send you the results after a few days to a week.
So the below price of the top-rated kit I used and recommend is an all-in cost. Everything is included in the price, including return shipping and lab analysis/result report.
I used the below Accustar long-term Radon test kit to determine that my home here in Upstate South Carolina has a slightly above national average Radon Gas level.
This is not surprising since this area is in the foothills of the southern Appalachian mountain chain, and thus is rich in fractured granite rock (in fact, Blue Granite is the South Carolina state stone). Granite often contains the black Uranium-containing mineral called "Hornblend" which can emit Radon gas. This is also why some granite counter-tops have been found to emit relatively high levels of Radon gas into homes.
Geology below and around your home can greatly affect how much Radon Gas is present and how easily it can infiltrate into your home from below. High risk Radon areas tend to have a lot of fractured granite stone, but not in all cases. Assumptions are not wise. The EPA recommends everyone test their home regardless of what state or region you live in.
Indoor Radon levels often fluctuate significantly due to many other variables. In higher risk zones, more frequent testing throughout the years would be wise, both short and long-term. This is why homeowners frequently opt for the below industry leading electronic radon gas detector so they get real-time feedback on these fluctuations with averages over shorter and longer term periods of time and for cost-savings compared to repeated passive testing over the years.
Note: the EPA defines short-term radon testing as 2 to 90 days duration, and long-term as 91 to 365 days duration.
Best Radon Testing Kits and Digital Radon Detectors for Measuring Radon Gas in Your Home - Use Arrows to Scroll Through All the Current Deals
What is Radon Gas? Where Does it Come From?
What is Radon gas?
It is a natural gas byproduct of the radioactive decay of Uranium which is found naturally inside the earth. Radon is itself radioactive and decays to hazardous atomic products such as Lead.
Radon is released from rocks, soil, and water and can accumulate to hazardous levels in your indoor air. Homes with dangerously high levels of Radon may be found throughout all 50 U.S. states.
Will I know if I inhale Radon Gas?
Radon is colorless and odorless. You can't smell airborne Radon as you inhale it. Nor can you taste it in instances when it's dissolved in well water.
Deadly Radon effects often take years of inhalation to manifest. But you can't tell when you are breathing it into your lungs day to day. Unless you already have a respiratory condition, Radon inhalation is not likely to produce immediate noticeable allergy symptoms or any noticeable short-term acute health problems. But serious health consequences can occur over the long-term, even leading to death by cancer.
Think about Radon inhalation in terms of getting X-rays or CT Scans done
You don't really feel any harmful effects from the radiation doses you get while being X-rayed or CT scanned. But damage is still being done on a bio-molecular level. You can't feel your cellular DNA being mutated, but it is still happening. This is the insidious nature of radiation exposure. Over time, exposure to excess radiation could lead to cancer as the damage to DNA accumulates or escapes repair. So limits are placed on dose and frequency of CT scans and X-rays.
Radon health effects are similar, but daily indoor exposure to regular radiation doses and toxic decay daughters, such as Lead atoms, efficiently target your lung tissue over time. It's a serious public health issue no one should ignore, no matter where you live or what your neighbor's level is. Even Radon-resistant buildings should re-tested periodically.
Radon gas inhalation is THE LEADING cause of Lung Cancer deaths in the U.S. among non-smokers, and it is the second leading cause among those who smoke cigarettes. Radon inhalation is believed to cause over 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year! This is why some states and the federal government are trying to raise even more awareness of the dangers of elevated Radon gas and why it is important for all homes to be tested.
Where does Radon come from?
The radioactive gas seeps up out of the ground and often enters homes through cracks, holes, pores or spaces in walls, foundation, slabs, basements or around pipes or from bare earth in crawlspaces. Radon has also been known to be released by some types of building materials such as certain granite counter tops.
Since the gas molecules are tiny, they can easily diffuse upwards through tiny spaces in building structures and thus into your home's living spaces from below. The more air-tight your home, the higher the concentrations may be depending on where you live and other variables.
Radon in Water?
Radon gas may also be carried into some homes via well water. It can then diffuse out of the water and into your indoor air (for example, during a steamy shower). Some will remain dissolved in the water too. Radon laden water consumption may increase the risk of such illnesses as Stomach Cancer. But the risks from Radon in ground water are considered of much less concern than inhaled Radon gas.
Testing for Radon in Water
If you test your indoor air and find high levels of Radon, and you also obtain your water from a well, then you should definitely consider also testing your water for Radon since airborne and water-borne Radon share the same geological source below/around your home.
State recommendations for water-borne Radon are spotty. But the EPA has proposed regulations for reducing Radon in private well water, with a likely recommended action level of 4,000 pCi/L.
You can find a certified Radon testing lab for measuring levels of radiation in water by calling the EPA Safe Drinking Water Hotline @ (800)426-4791.
Water Radon Removal Systems
Depending on the level of detected Radon in water, two main types of Radon reduction system are commonly used: 1.) Aeration systems, or 2.) Granular Activated Carbon Systems (EPA does not recommend GAC systems when water Radon is >5,000 pCi/L).
For more information about Radon:
Check out my guide to this deadly radioactive gas.
 Call 1-800-SOS-RADON for help from the EPA
Call 1-800-SOS-RADON for help from the EPAWhy Should I Test My Home for Radon Gas?
You are likely breathing some level of Radon gas and its toxic decay products as you are reading this. But no need to panic just yet. We evolved amid background radiation levels from Earth, so low levels of radiation is just a natural, and probably even essential, part of being an Earthling. In fact, I recall some evidence of microscopic organisms being observed to develop abnormally in a radiation-free environment.
The problem in modern times is our modern air-tight homes planted in or on the ground, and thus becoming like accumulating bubbles of higher than normal concentrations of many potentially toxic compounds, molecules, and atoms which can lead to biologically dangerous levels of exposure. This is often the case with Radon.
Radon is virtually everywhere, but some homes are dangerously high in Radon compared to others and this can significantly increase your risk of dying from Lung Cancer. The American Lung Association, World Health Organization, U.S. Surgeon General, and EPA have deemed Radon exposure to be a leading cause of lung cancer.
The EPA estimates that at least 1 in 15 homes in the U.S. have dangerously elevated levels of Radon. And this is no small matter since it's believed Radon can be up to 6 times more destructive to your lungs than is secondhand cigarette smoke.
Smoking Cigarettes + Radon = Risk Greater Than Sum of Parts
If you smoke cigarettes and your home has high Radon, your risk of lung cancer is greater than the sum of the risks from either.
By the way, did you know cigarette smoke also delivers significant doses of radiation from different atomic sources known as Polonium-210 and Lead-210?
Polonium 210 and Lead-210 are radioactive isotopes which occur naturally in the soil and air and which are also found in high-phosphate fertilizers used to grow agricultural crops, such as tobacco used to manufacture cigarettes or smokeless tobacco products like dip or chewing tobacco.
These radioactive materials are absorbed by tobacco plants and can also stick to the surface of the tobacco leaves, such as when soil dust becomes wind blown. So in addition to the cyanide, nicotine, tar, and arsenic in tobacco smoke, these radioactive materials get trapped inside the fine passages of the lungs and bronchiol tubes once inhaled by smokers or those inhaling their secondhand smoke.
These radioactive particles continuously release radiation which damages surrounding tissue cells further, eventually contributing to cancer and a host of other respiratory illnesses and symptoms.
The irony of it is that even these sources of radioactivity and toxic metals ultimately likely came from the natural decay of Uranium-238, and thus the decay of Radon, as you can see by the below chart of radioactive decay products and half-life. So even if a smoker's home is low in Radon, if they smoke they are still injecting Radon daughters and radiation directly into their respiratory system.
The Rad Badge Incident
In the laboratories in which I worked cigarette smoke radiation became evident when all the smokers were flagged for high radiation exposure.
Most lab personnel had to wear what are called "Rad badges" which are worn on lab coat lapels to measure dose of radiation from our XRF instruments over time. At one point a group of lab personnel had their Rad Badges flagged for high radiation after they were tested by an independent lab.
As it turned out, the radiation source was due to the badges being exposed to cigarette smoke during smokers' regular smoke breaks outside.
At first, we thought there was a radiation leak from the instrument. But on further inspection the correlation with those who took frequent smoke breaks became evident. This was likely caused by the Lead-210 and Polonium-210 isotopes contained within their cigarette smoke.
Think about it, smokers are regularly and efficiently dosing their lungs and bronchial tubes with radiation and heavy metals from tobacco Polonium-210 and Lead-210. This directly damages lung tissue via radiation AND toxic elements, on top of the tissue damage caused by all the other chemical pollutants in cigarette smoke. Add to this lung damage from any Radon levels at home, and yes smokers inhaling Radon gas are indeed in double jeopardy.
If you smoke cigarettes you are effectively committing slow suicide. And some selfish people who regularly smoke indoors may be committing slow HOMICIDE of any occupants (such as children) forced to breath the secondhand smoke, especially in the presence of indoor Radon.
Smoke particles are thought to also assist the damage from Radon because the tiny smoke particles attract and help carry the Radon decay atoms deep into the lungs which further magnifies the potential for tissue damage upon inhalation.
I know a few selfish parents who still insist on smoking around their kids. They all fell for the well-documented P. Morris psychological tactic designed to attract and quickly addict people based on the "I'm a cool rebel" mentality. This carefully designed psycho-social marketing strategy was personified in ads in the form of the rugged individualist called "The Marlboro Man".
Many of these smokers' kids have already developed asthma, a life-long debilitating respiratory disease, as a result of inhaling their parents' secondhand smoke.
As a child I too was the victim of years of secondhand smoke exposure from relatives and others I was often in the care of. Luckily, despite exposure to second-hand smoke during my early years, I never picked up the habit. I tried cigarettes as a teen, but as Clinton said, I never inhaled. I just didn't like the feel of the smoke in my lungs.
Radon Concentrations and Units of Measurement in U.S.
Airborne Radon is measured in terms of detected radioactive decays per unit volume of air, which is represented as units of picoCuries per Liter of air (pCi/L). In the U.S. indoor Radon levels tend to average about 1.3 pCi/L, while outdoor levels tend to average about 0.4 pCi/L.
Inside Radon levels can vary greatly based on factors such as home design, substructure geology, seasonal weather patterns, barometric pressure, degree of ventilation, ect. It is recommended that you test your indoor air for Radon at least every 2 years and follow directions carefully to assure accurate readings each time.
All homes and buildings, whether built Radon-resistant or not, should be tested. This includes schools, day care centers, work places, apartment buildings, ect.
The below Radon monitor will give the most accurate result since it can give you a longer term average. It also provides immediate feedback on how increasing ventilation, such as by opening windows and turning on window fans, can quickly reduce Radon levels (though these are only temporary fixes and no substitute for professional Radon repair).
If your home is found to have levels greater than or equal to 4 pCi/L, it is recommended by the EPA and U.S. Surgeon General that a Radon fix would be wise. But because radioactive damage and decay products at the level of 2 - 4 pCi/L can still represent a significant hazard to long-term health, I have noticed the EPA is hedging to the downside and now recommends you think about Radon mitigation at even those lower levels.
Something else to think about...
The EPA estimates we 21st Century humans are spending as much as 90% of our time indoors, so given the huge volume of indoor air our lungs will process over many years indoors, it stands to reason that even low to borderline levels of Radon (2 - 4 pCi/L) may raise health risks significantly. This supports their more recent concerns about fixing even lower levels.
Radon levels are impossible to predict even on a very localized level. Even homes next to each other can vary greatly. Testing for Radon is cheap and easy. Since the risks of cancer can be high in many areas, the U.S. Surgeon General and EPA have recommended ALL homes be tested for radon gas.
The only way to know your home Radon level is to test for it with a passive test kit or using an active electronic radon gas detector. This page has information about the best Radon test kit and electronic radon gas meter. You can pay a very high priced local professional to come and test your home, but it will likely cost you 5 to 10 times or more compared to the below affordable and reliable diy Radon test kits.
What If My Radon Test Results Are High Enough to Require Mitigation?
If you test for Radon and find high inside levels requiring a fix, then Radon mitigation (consisting of various techniques for collecting and exhausting the gas from below your home using Radon fans) can be done relatively inexpensively.
Certified Radon Contractors/Mitigators usually perform a diagnostic evaluation followed by sealing of cracks and other entry points. Then a collection and exhaust system is installed under the footprint of the home.
The "Active Soil Depressurization system" (ASD) creates a low pressure gradient under the home using a Radon Sump and Radon exhaust fan to draw and vent the radioactive gas safely outside of the home.
But the first step is to test for it. And the last step after the fix is in is to test again to confirm everything is working as it should. Even if you buy a Radon-resistant home, you should still test. If it's found high an already mitigated home usually costs less to fix.
I have a bare earth crawlspace with vapor barrier in a fairly high Radon danger zone (Upstate South Carolina). So I was concerned I might have elevated levels of Radon indoors.
But my home has tested well below the EPA Radon action level of 4 piC/L. I performed a long-term Radon test consisting of 195 days of exposure of a passive activated carbon based kit placed within a bedroom of my house.
My reading ended up being 2.2 piC/L, so I'm not too concerned at this time. But I will keep monitoring the levels over the years and may consider some form of crawlspace Radon mitigation system for further peace of mind.
My friend in Ohio was not so lucky as I. When he decided to sell his home near Cincinnatti last year he had to get a Radon test done as part of the real-estate transaction. His home tested extremely high and he had to pay for professional Radon mitigation and further testing.
Luckily Radon repair is comparable in cost to other basic home renovations and repairs. My Ohio friend hired a certified Radon contractor (mitigator) who I believe charged him about $5,000 for the fix.
Your state Radon office can help put you in contact with highly qualified Radon mitigators in your area should you also require a fix for elevated levels. Or check your local Yellowpages.
If you are planning to have a new home built, give serious consideration to finding a builder or contractor who can build in radon‐resistant features. Keep all the documentation showing you took these extra steps to mitigate Radon levels. Should you plan to later sell the property, this proof will allow you to list this system as another selling point, and it may help the transaction go through more smoothly.
The Geology of Your Area Can Influence Your In Home Radon Gas Concentration
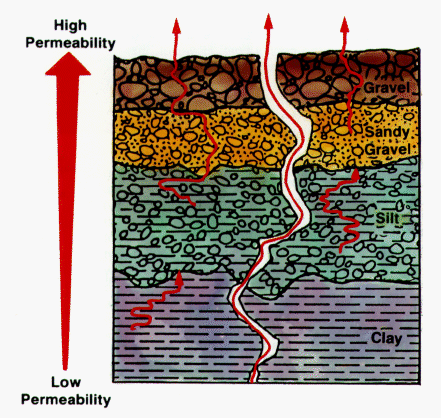 Radon Gas infiltration is greatly affected by the Geology of a particular area.
Radon Gas infiltration is greatly affected by the Geology of a particular area.Radon Gas Moves Upwards Through the Home On Air Drafts Wafting Through the Home
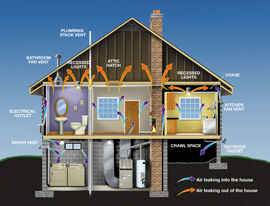
Air drafts wafting through the home via the chimney effect help to pull Radon Gas up from lower levels to higher floors of the home, though lower levels such as basements or the first floor may still often have overall higher detectable levels of Radon compared to the upper floors of a home. So Radon Gas detection is often done at the lowest actively lived in levels and where air drafts are minimal.
Keeping crawlspace vents open for increased crawlspace ventilation is important to help let Radon Gas flow outside rather than collecting and seeping upwards into the home. But this and a standard Vapor Barrier is still often not enough of a mitigation system for Radon reduction.
My house has a crawlspace where the gas can collect and filter up through the floor boards into the living space depending on pressure gradients (gases passively flow from high pressure to low pressure).
Houses with basements sunk into the earth also may be more likely to have elevated Radon Gas levels compared to houses with slab foundations. This is because the basement cavity creates a low pressure area compared to the surrounding earth and the Radon will flow down the pressure gradient taking the path of least resistence into the basement and up into the home carried by air drafts wafting up through the building structure.
The more air tight our homes become for the purpose of increased energy efficiency, the more Radon Gas they may tend to accumulate. But even still, no matter what style of home or how air tight it is, all homes should be tested for Radon Gas.
Why Testing for Radon Gas is so Important
Deaths from Radon Gas Exposure
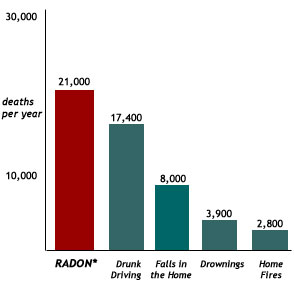
As you can see from the above chart of Radon deaths compared to other causes of deaths in the U.S., Radon Gas exposure is implicated in almost as many deaths as those caused by drunk-driving accidents and drownings combined.
The following quote is from Elizabeth Hoffmann a victim of Radon cancer and the co-founder and former president of Cancer Survivors Against Radon (CanSAR).
Unfortunately, Mrs. Hoffmann passed away on November 6, 2013 after her multi-year battle with lung cancer.

There really is no safe level of Radon exposure. Any Radon exposure, even below the recommended action level of 4 pCi/L, means some increased risk of cancer for most. In fact, your risk of Lung Cancer is estimated to rise about 16% with every 2.7 pCi/L increase in Radon Gas exposure. But if you smoke the risk will likely be much greater.
This increased cancer risk is why it is so important to know how to test for Radon Gas. Once you know your level, you can decide if Radon abatement is needed, then take mitigation actions to protect your health.
Radon is a serious chronic health hazard, but some homeowners ask about "Radon Poisoning", as if inhaling it produces immediate acute health affects like those of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning.
Radon is colorless, odorless, and usually produces no immediate allergy symptoms when inhaled. You probably would never know you are breathing it. A Radon test is the only way to confirm the probability that you may be inhaling it.
Any symptoms suspected to be related to so-called Radon Poisoning are probably most noticeable as a result of the cumulative damage caused by smoking in conjunction with elevated Radon levels.
Emphysema, Pulmonary Fibrosis, COPD, Interstitial Pneumonia, persistent cough, breathing difficulty, weight loss, wheezing, infections, and Hyperglycemia can all be worsened long-term by exposure to elevated levels of Radon Gas which introduces both toxic metals and radiation directly into the lung tissue. So "Radon Poisoning" via the air eventually may lead to Lung Cancer due to this damage. And Radon in Water may result in Stomach Cancer.
Radioactive Decay of Uranium-238 Leads to Radon Gas With Further Decay Producing Alpha and Beta Radiation and Other Toxic Radon Daughter Elements
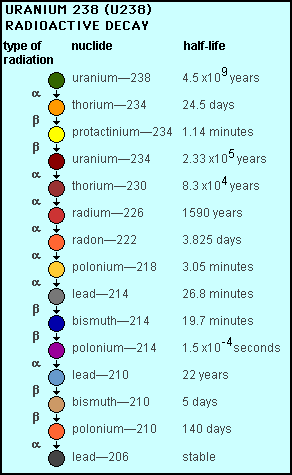
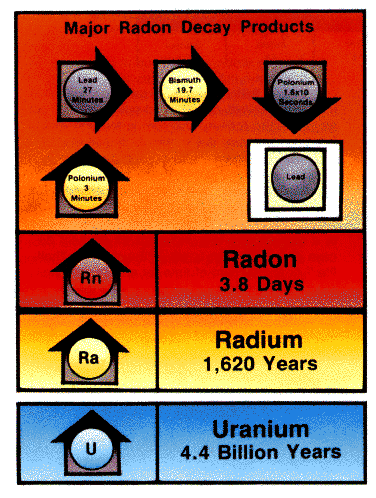
As you can see from the above charts of Radon Daughters, radioactive decay of Uranium-238 within the Earth's crust can ultimate result in the heavy metal Lead and doses of radiation directly into your lungs, especially if Radon Gas levels are elevated in your home.
Tips for Getting the Most Accurate Results With Your Radon Test Kit:
- Limit Air Exchange
test during any season, but for short-term tests try to limit air drafts by keeping all windows, external doors, and vents to the outside closed for 12 hours before you start your test and through to the end of the test period. For short-term tests this may mean several days. - Keep Doors to Outside Closed
you can still follow your normal routine of exiting and entering your home, just be sure to close doors behind you when exiting or entering to limit air exchange which might dilute Radon and thus skew your actual result falsely low. - Indoor Equipment
you can still follow your normal operating schedule for equipment such as dehumidifiers, furnace combustion air supply, air-to-air heat exchangers, central air-conditioning, and/or an existing Radon mitigation system. Just try to avoid using things like a whole-house ventilator, such as attic fan, or window fans. These can exchange indoor air with the outside, thus possibly diluting indoor Radon levels, thus giving a falsely low reading. - Weather Conditions to Avoid
some people with electronic radon monitoring meters have noted their levels tend to go up during rainy weather. This could be due to low barometric pressure increasing Radon gas "suction" effect from the earth. Or airborne water molecules (increased humidity) might also affect charge-related measurements. So it might be wise to try and avoid testing during extended severe weather or strong storms which can produce strong winds (>25 mph) and low barometric pressure for more than 24 hours. More than a day of these conditions may skew your short-term indoor Radon level. You want to measure typical levels over the duration of the test. - Real Estate Transactions
If you are using this as Real Estate Radon Test Kits place two kits beside each other, with about 6 inches between. Don't disturb the kits for the full duration of the test period. Test the lowest level of a building to be used by a potential buyer. - Optimal Rooms for Test Kit Placement
Always test the lowest livable area of a building, preferably in a room where the test kits will be less likely to be disturbed. Ideal rooms to test in are: bedrooms or living rooms/dens. - Consider Hanging Test Kit from Ceiling
For optimal air exposure consider hanging the test kit in the middle of a room using a piece of string so the kit hangs at normal breathing height 2 to 6 feet from the floor. - Avoid Testing in Drafty Locations
Don't test for radon in rooms with any type of operating blower or fan. Don't place test kit within 3 feet of these possible sources of air drafts: AC duct vents, doorways, windows, hallways, or exterior walls. Moving or blowing air can produce a falsely high Radon result. - Avoid Testing Near Heat Sources
Sources of heat may produce a falsely low Radon result. So try to avoid placing the kit in direct sunlight, and avoid heat sources such as: fireplace, baseboard heaters/radiators, space heaters, or stoves. - Avoid Testing In High Humidity Areas
Rooms with >50% Relative Humidity can produce an inaccurate Radon result. So avoid testing in rooms that tend toward having higher humidity levels, such as: laundry rooms, kitchens, bathrooms, closets, and basements. It is not recommended to test in crawlspaces either, except maybe in cases where a previous indoor result was high and subsequent testing is for investigating possible entry points. If testing in areas where RH is >50%, then test only for the shortest recommended duration. - Avoid Missing or Unreadable Information
The radon test labs process millions of test kits and will confirm they receive thousands of kits which have missing or unreadable information. If your writing can't be read, or if your information is incomplete, it may cost you an extra reprocessing fee to get your results, if you can get them at all. Not providing test dates and times will likely invalidate your test results. - Send the Kit to the Lab ASAP, here's why...
Radon is unstable and undergoes radioactive decay. As you can see in the above chart the half-life of radon is only 3.825 days. So the longer you wait to send back your test kit for analysis, the less Radon will remain for detection by the lab, and thus you may only get an estimated result. If it takes more than 12 days to get the kit back, the lab likely won't be able to provide any result due to excessive radioactive decay of the Radon. - Follow Your Specific Test's Instructions Carefully
No matter what tips I've shared above, each test kit is different and you should follow that kit's specific instructions and recommendations.
Best Radon Testing Kits and Digital Radon Detectors for Measuring Radon Gas in Your Home - Use Arrows to Scroll Through All the Current Deals
See more tips for reducing your exposure to Radon Gas








New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.